Does Opting Out of Data Brokers Really Work Exploring the Effectivenes…
페이지 정보

본문

In the digital age, our every online move is tracked and catalogued, often without our explicit consent. This section delves into the strategies individuals employ to reclaim their digital footprint, questioning the efficacy of these methods. Are the efforts to shield our data from pervasive collection truly impactful, or are they merely a drop in the ocean?
Understanding the Mechanisms of Data Protection
As we navigate through the vast digital landscape, the quest to safeguard our personal details becomes paramount. This article examines the various approaches one might take to limit the dissemination of their sensitive data. It explores whether opting for exclusion from these extensive databases is a viable solution or if it merely provides a false sense of security.
Challenges in the Realm of Digital Privacy
The complexity of modern data management systems presents a formidable challenge. This discussion highlights the intricacies of data privacy and the potential pitfalls of attempting to withdraw from these comprehensive data repositories. It questions the practicality and effectiveness of such measures in an era where data is considered a valuable commodity.
Understanding Data Brokers and Their Role
This section delves into the intricate mechanisms that facilitate the collection of user details by various entities in the digital realm. It aims to clarify how these entities gather and manage vast amounts of user-related data, shedding light on the processes that underpin the digital economy's data-driven nature.
Data collection mechanisms vary widely, depending on the source and the intended use of the information. Here are some common methods employed:
- Web Tracking: Utilizing cookies and other tracking technologies, companies monitor user activities across websites, collecting browsing habits and preferences.
- Social Media Monitoring: Platforms analyze user-generated content and interactions to compile profiles that can be used for targeted advertising and other purposes.
- Transactional Data: Every purchase, subscription, or financial transaction leaves a digital footprint, which is often collected and analyzed.
- Public Records: Data from government records, such as property deeds or court documents, are also harvested for various uses.
- Surveys and Feedback: Direct user input through surveys or feedback forms provides another rich source of personal data.
Each of these methods plays a crucial role in building a comprehensive profile of individuals. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for users to grasp the extent of their digital footprint and the implications for their privacy and security.
Moreover, the data collected is not static; it is constantly updated and cross-referenced with new information, enhancing its accuracy and utility for those who manage and trade in such data.
In conclusion, comprehending the mechanisms of data collection is vital for anyone concerned about their digital privacy and the use of their personal details. It empowers users with knowledge about how their information is gathered, processed, and potentially exploited, thereby enabling more informed decisions about their online activities and privacy settings.
The Mechanisms of Data Collection
This section delves into the intricate processes through which entities gather details about individuals. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for grasping how such information is subsequently used and managed.
Data collection typically involves several methods, each tailored to specific needs and contexts. Below are some common techniques employed:
- Surveillance: Continuous monitoring of activities, often through digital means such as tracking online behavior or using CCTV cameras.
- Transactional Data: Information automatically generated from transactions, including purchases, bookings, or financial exchanges.
- Self-Reported Data: Details provided directly by individuals, such as through surveys, forms, or registrations.
- Sensor Data: Information collected via sensors, including GPS location data, biometric data, or environmental data.
- Public Records: Data available in public domains, such as government records, property records, or court documents.
Each method has its own implications for how information is gathered, stored, and potentially shared. For instance, surveillance data can be highly detailed but also raises significant privacy concerns. Transactional data, while less personal, can still reveal patterns of behavior that might be sensitive.
Understanding these mechanisms not only helps in recognizing the sources of data but also in evaluating the potential risks associated with data collection practices. It is essential for individuals and organizations alike to be aware of these processes to make informed decisions about data privacy and security.
How Data Brokers Utilize Personal Information

In this section, we delve into the intricate ways in which entities that aggregate and manage vast amounts of user details operate. Understanding their methodologies is crucial for comprehending the broader implications of data management in today's digital landscape.
These entities, often referred to as information aggregators, collect a plethora of user details from various sources. This includes but is not limited to browsing history, purchasing patterns, and social media activity. The gathered data is then processed and analyzed to extract patterns and insights, which are subsequently used for targeted advertising, risk assessment, and other commercial purposes.
The utilization of this data extends beyond mere advertising. It plays a significant role in credit scoring, employment screening, and even in the determination of insurance premiums. By leveraging detailed profiles, these aggregators can provide businesses with a comprehensive view of potential customers or risks, thereby influencing critical decisions in various sectors.
Moreover, the rise in the use of personal data has sparked significant concerns regarding user privacy and data security. As these aggregators continue to expand their reach and refine their data collection techniques, the potential for misuse or breaches of sensitive information increases, leading to heightened public anxiety about the safety and sanctity of personal data.
In conclusion, the role of information aggregators in the modern digital economy is multifaceted and influential. Their methods of data utilization have profound implications for individual privacy and corporate strategy, making it essential for both consumers and businesses to understand and navigate this complex landscape.
The Rise of Privacy Concerns
In recent years, there has been a significant escalation in public awareness regarding the protection of sensitive details. This section delves into how societal recognition of the importance of safeguarding private details has evolved and its implications on various practices.
Initially, the issue of confidential detail protection was not a mainstream concern. However, as incidents of unauthorized access and misuse of these details have become more prevalent, public sentiment has shifted dramatically. Here are some key factors that have contributed to this heightened awareness:
- Increased media coverage of breaches involving unauthorized access to confidential records.
- Growing public understanding of the value and vulnerability of their own confidential records.
- Legislative actions and regulations aimed at enhancing the security of confidential records.
- Advocacy by privacy rights groups highlighting the risks associated with the uncontrolled sharing of confidential records.
The impact of this increased awareness is multifaceted. On one hand, it has led to more stringent regulations and practices aimed at protecting confidential records. On the other hand, it has also spurred innovation in the field of security technology, with a focus on developing more robust methods to safeguard these records.
Furthermore, public awareness has also influenced consumer behavior. Individuals are now more cautious about sharing their confidential records, and they scrutinize the security measures of entities requesting such information. This shift in consumer behavior has forced businesses to prioritize the protection of confidential records in their operations.
In conclusion, the rise of concerns over the protection of confidential records is a complex phenomenon driven by a combination of technological advancements, legislative changes, and societal awareness. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for anyone involved in handling or protecting confidential records.
Public Awareness and Its Impact on Data Practices
This section delves into how increased consciousness among the general populace influences the methods and policies employed by entities in the digital realm. As understanding grows regarding the collection and use of digital footprints, there is a noticeable shift in how these practices are regulated and perceived.
Awareness campaigns and educational initiatives have played pivotal roles in shaping public opinion and, consequently, the strategies of organizations dealing with user data. The impact of such awareness can be seen in the increased scrutiny of data handling practices and the demand for more transparent and ethical data management.
| Aspect of Awareness | Impact on Data Practices |
|---|---|
| Increased Demand for Transparency | Organizations are now more inclined to disclose their data collection and usage policies, aiming to build trust with users. |
| Shift in Legal Frameworks | New regulations and laws are being developed or amended to reflect the public's concerns about data privacy and security. |
| Consumer Behavior | Users are becoming more selective about the services they use, often choosing those that offer better data protection and privacy assurances. |
| Innovation in Data Handling | Companies are investing in technologies and practices that enhance data security and privacy, driven by consumer expectations and regulatory pressures. |
The interplay between public awareness and data practices is complex and dynamic. As awareness continues to rise, it is likely that we will see further evolution in how data is collected, used, and protected. This ongoing dialogue is crucial for fostering a digital environment that respects and safeguards individual rights.
Legal Frameworks Governing Data Privacy
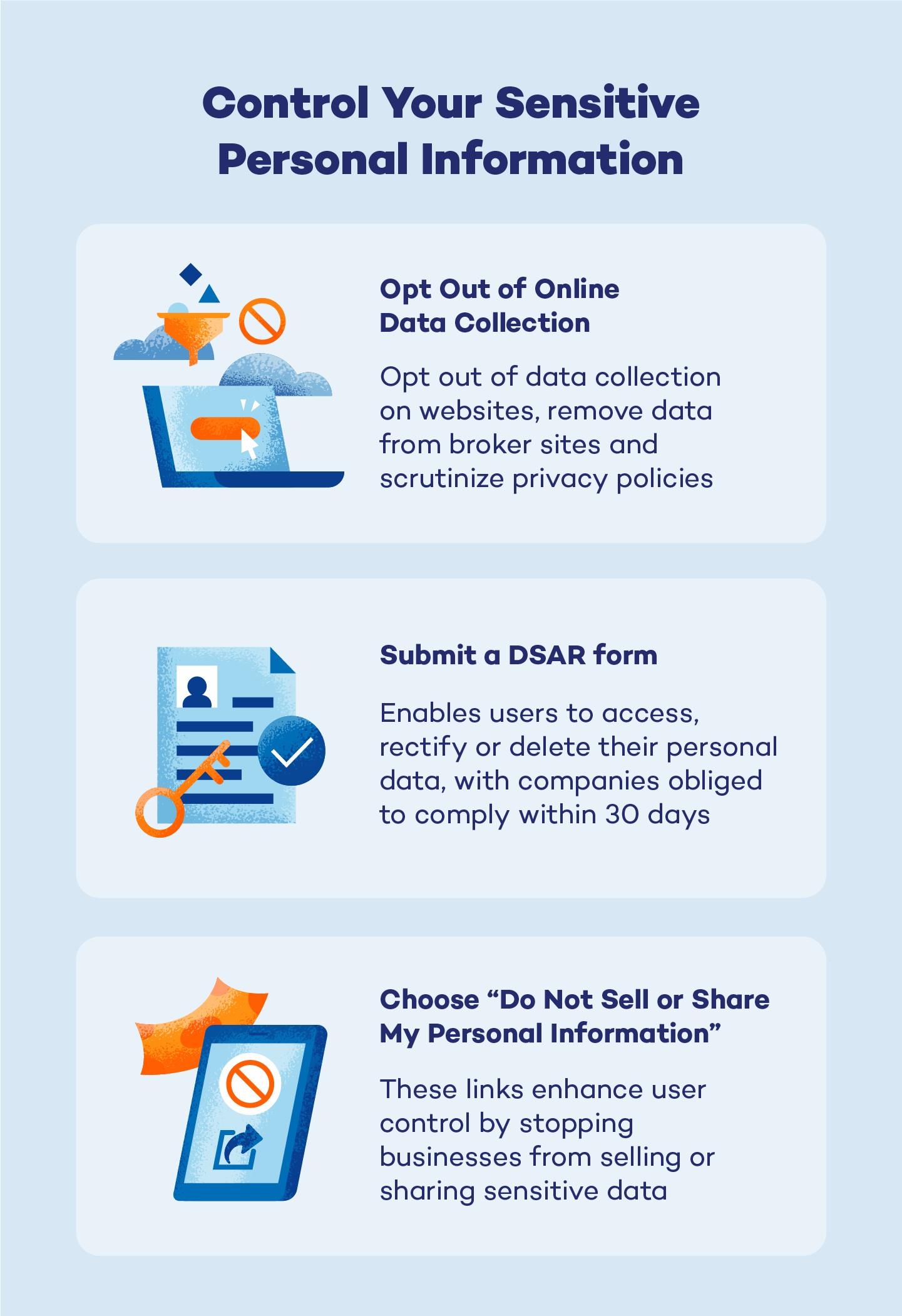
This section delves into the regulatory structures that oversee the protection of sensitive user details. It examines how various laws and policies aim to safeguard individual rights concerning their digital footprint.
In the realm of digital privacy, several key legal frameworks have been established to regulate the handling of user data:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This European Union law sets stringent standards for the collection, processing, and storage of personal data. It grants significant rights to individuals, including the right to access and erase their data.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Enacted in the United States, this act provides California residents with the right to know what personal information is being collected about them, to opt out whitepages out of the sale of their personal information, and to request deletion of their data.
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA): In Singapore, this law governs the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data. It also emphasizes the accountability of organizations in ensuring data privacy.
These frameworks not only define what constitutes personal data but also outline the responsibilities of entities that handle such data. They typically include provisions for:
- Transparency in data collection practices
- Consent requirements for data usage
- Security measures to protect data
- Rights of individuals to access, correct, and delete their data
Understanding these legal structures is crucial for both individuals and organizations. For individuals, it empowers them with knowledge of their rights and how to enforce them. For organizations, compliance with these laws is not only a legal obligation but also a critical component of building trust with users.
In conclusion, the legal frameworks governing data privacy play a pivotal role in shaping the digital landscape. They provide a foundation for ethical data practices and ensure that the rights of individuals are protected in the digital age.
Opting Out: A Practical Guide
This section provides a comprehensive roadmap for individuals seeking to manage their digital footprint by reducing the availability of their details on various platforms. It outlines practical steps and considerations to effectively navigate the process of minimizing exposure of one's details online.
Identify the Sources: The first step involves identifying where your details are being held. This could range from online directories to more obscure databases. A thorough search using your name, email address, and other identifiers can help pinpoint these sources.
Request Removal: Once identified, the next step is to request the removal of your details. This typically involves contacting the service directly through their provided channels, often found in their privacy policy or contact section. It is crucial to follow the specific instructions provided by each service to ensure compliance with their removal procedures.
Verification Process: Many services require verification of identity before they remove your details. This might involve providing a copy of a government-issued ID, a utility bill, or responding to a verification email. Ensure that any sensitive information is shared securely and that the service has robust privacy measures in place.
Follow-Up: After submitting your request, it is important to follow up regularly. Some services may take longer than others to process removal requests. Keeping track of your communications and the status of your requests can help ensure that your details are indeed removed.
Monitor Your Presence: Even after successfully removing your details from certain platforms, it is advisable to periodically check to ensure that your details do not reappear. New services and databases may emerge, and old ones may change their policies. Regular monitoring helps maintain control over your digital presence.
By following these steps, individuals can significantly reduce the visibility of their details online, enhancing their overall control over their digital identity and mitigating potential risks associated with data exposure.
Steps to Remove Personal Data from Brokers
This section delves into the practical steps individuals can take to mitigate the exposure of their sensitive details held by third-party aggregators. While the process can be intricate, understanding the key actions can significantly aid in reducing the visibility of one's private details on the internet.
- Identify the Aggregators: Begin by compiling a list of all known entities that collect and distribute personal details. This involves researching and identifying these organizations.
- Access Removal Policies: Each aggregator typically has its own set of rules and procedures for data removal. Familiarize yourself with these policies to understand the requirements and limitations.
- Prepare Necessary Documentation: Some aggregators may require proof of identity or other documentation to process a removal request. Ensure you have all necessary documents ready to expedite the process.
- Submit Removal Requests: Follow the specific instructions provided by each aggregator to submit your request for data removal. This may involve filling out online forms or sending emails.
- Monitor Responses: Keep track of all communications from the aggregators. Some may respond quickly, while others may require follow-ups. Document all interactions for future reference.
- Follow Up Regularly: If your initial request does not result in the removal of your details, consider scheduling regular follow-ups. Persistence is key in ensuring your data is removed.
- Utilize Legal Avenues: If the aggregators do not comply with your requests, explore legal options. This might involve consulting with a legal expert to understand your rights and the potential for legal action.
- Educate and Protect: Continue to educate yourself on new aggregators and data collection practices. Implement protective measures such as using privacy tools and reading terms of service carefully to prevent future data collection.
By following these steps, individuals can take proactive measures to control the dissemination of their private details by third-party entities. It is important to remain vigilant and persistent in these efforts to effectively manage personal data visibility.
Common Challenges in the Opt-Out Process
This section delves into the various obstacles individuals face when attempting to limit the distribution of their sensitive details across digital platforms. Despite the growing awareness and tools available, the process of removing one's data from these repositories is fraught with complexities and hurdles.
- Incomplete Information: Often, the details provided about how to exclude oneself from these databases are insufficient or outdated, making the process confusing and inefficient.
- Multiple Platforms: Individuals must navigate a myriad of different sites and services, each with unique procedures and requirements, which can be time-consuming and frustrating.
- Lack of Transparency: Many of these services are not transparent about what data they hold or how it is used, complicating the task of identifying where to begin the exclusion process.
- Persistence of Data: Even after successful exclusion, data can persist in various forms across the internet, requiring ongoing vigilance and repeated efforts.
- Legal and Regulatory Gaps: In many regions, there are insufficient laws or regulations to enforce data removal, leaving individuals with limited recourse.
Understanding these challenges is crucial for anyone seeking to protect their digital footprint. It highlights the need for both improved personal strategies and broader systemic changes to enhance data protection practices.
Assessing the Effectiveness of Opting Out
In this section, we delve into the evaluation of the efficacy of withdrawing from certain practices that involve the collection and dissemination of individual details. This analysis aims to determine how successful these withdrawal strategies are in reducing the exposure of one's sensitive details online.
Challenges in Removal Processes: The act of requesting the deletion of one's records from various platforms can be fraught with obstacles. These include complex procedures, lack of transparency, and the persistence of data even after requests have been made. It is crucial to understand these hurdles to gauge the overall success of such removal efforts.
Impact on Data Accessibility: A key measure of the effectiveness of these withdrawal methods is the extent to which they diminish the accessibility of one's data. This involves assessing whether the data is truly removed or merely hidden from immediate view, potentially still retrievable through other means.
Long-term Effects: Evaluating the long-term impact of these withdrawal strategies is essential. This includes observing whether the reduction in data visibility is sustained over time or if there are recurrences of data exposure due to lapses in data protection practices or new data collection methods employed by entities.
In conclusion, while the act of withdrawing from data collection and dissemination practices offers a semblance of control over one's digital footprint, its effectiveness varies widely depending on numerous factors. It is imperative for individuals to remain vigilant and informed about the evolving landscape of data privacy to truly safeguard their sensitive information.
Long-Term Impact on Personal Data Visibility
Assessing the long-term consequences of removing one's details from information aggregators is crucial for understanding the overall efficacy of such actions. This section delves into how effectively individuals can diminish their digital footprint and the lasting effects of these efforts.
Initially, the process of erasing one's records from various platforms might seem straightforward. However, the reality is often more complex. Persistent visibility of personal details can be attributed to several factors, including the resilience of data networks and the persistence of secondary sources that continue to disseminate information.
One significant challenge is the dynamic nature of data circulation. Even after successfully requesting the removal of personal data from primary sources, secondary or tertiary platforms might still retain and display this information. This can occur due to data sharing agreements or automated data scraping practices, which are prevalent in the digital ecosystem.
Furthermore, the legal frameworks governing data privacy and the rights of individuals to control their information vary significantly across jurisdictions. This variability can complicate the process of data removal and its long-term effectiveness. In some regions, robust legal protections facilitate easier and more permanent data erasure, while in others, the legal landscape is less supportive.
Public awareness and advocacy play pivotal roles in enhancing the effectiveness of data removal efforts. As more individuals become aware of the implications of their data being publicly accessible, there is a growing push for stricter regulations and more transparent data practices. This awareness can lead to legislative changes that empower individuals to more effectively manage their digital presence.
In conclusion, while the act of removing one's data from information aggregators can have immediate benefits, the long-term impact is influenced by a multitude of factors, including technological, legal, and societal changes. Continued vigilance and advocacy are essential to ensure that personal data visibility is effectively managed over time.
- 이전글비아그라 성분-시알리스 처방전 없이 구입-【pom5.kr】-자유로운 24.07.13
- 다음글Bitcoin News ? Classes Discovered From Google 24.07.13
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.

